What is Data Governance, and Why is it Important?
In today's digital age, data is essential to any organization. It is the backbone of decision-making, customer engagement, and overall business operations. However, with great power comes great responsibility. The sheer amount of data organizations generate, and store can be overwhelming, making it challenging to manage and protect. This is where data governance comes in. This article will discuss data governance and why it's crucial for businesses and organizations in the 21st century.
Data is essential for businesses as a critical asset to support a company's strategy, growth, and survival. Data knowledge's extensive use and reuse can deliver internal and external business performance improvement (Business Processes), provide the appropriate answer to business regulations, and create new disruptive opportunities with artificial intelligence based on good Data.
You must organize your company, build knowledge on your actual company data, and promote data reuse to deliver the value connected to your data potential. Data is vital for businesses as a critical asset to support a company's strategy, growth, and survival.
Discover the essential topics you need to know to make your data governance program successful!
What is the definition of data governance?
Data Governance is a set of processes, rules, and standards that ensure the high quality of data and its integrity throughout an organization. It helps organizations to ensure that their data is accurate, complete, secure, and consistent.
Data governance is a top-level business initiative with specific goals:
define a data governance strategy based on the company strategy, business priorities, and critical uses cases and,
define and manage how to implement this strategy to deliver value.
Data Governance aims to organize roles between business users (Data users and Data owners), IT department, and support teams (Data Office). Their objective is to create a data practice community and build necessary data knowledge at a business language level – based on the actual data in systems (Data management). This asset must be easy to access and reusable for any Business or Data Scientist to help communicate and promote Data Governance initiatives, its progress, and successes in establishing Data Literacy and Data Culture in the company.
What is Data Governance Process?
The Data Governance Process is managing the availability, usability, integrity, and security of data used in an organization.
It involves creating policies and procedures that define how data is collected, stored, accessed, and used by different stakeholders. Data Governance processes also ensure that all stakeholders know the rules and regulations governing data usage.
Data Governance helps organizations ensure compliance with laws, regulations, and industry standards while protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. Additionally, it helps ensure that data is accurate and up to date so that decisions are based on reliable information.
Roles: who is responsible for the enterprise data governance success?
Data Governance success relies on joint teamwork animated by the CDO with Business data users, data owners, and I.T. stakeholders (I.T. Department, Enterprise Architecture and Business Processes managers, Data Protection Officers, R&D, and Innovation leaders).
The Chief Data Officer's mission is to help the organization leverage data as a strategic asset and support and animate the data community. In a company, the board of directors will define a vision, a strategy, and critical business objectives and use cases. Within the organization, even though every company is unique, here are the four most common data governance roles:
Chief Data Officer (CDO)
The Chief Data Officer (CDO) leads the data governance program – with his Data Office Team, and is responsible for its success. He usually directly reports to the CEO and interacts with the board of Directors as a critical stakeholder.
The CDO's objective is to master data knowledge, set up compliance with regulations, and provide data reuse and innovation ability, such as A.I.
Data Office Member
Data Owners
The data owner is responsible for the data. Typically, as part of the business team, he is the principal contact for specific operational data. He uses data and benefits from data sharing. His primary objectives are to be a data domain expert and to create data reuse projects for his domain and the whole company. A data steward helps him.
Data Stewards
The data steward holds the knowledge of the data and its metadata. He helps organizations set up data governance projects and improve data literacy. His primary objectives are making meaningful data catalogs and business glossaries for data reuse and Innovation and supporting data reuse projects.
They fill the gap between I.T. (Information Technology) and business, and by doing so, they improve collaboration and data usage.
Partners
Data Architect
Data architects create and model the organization's databases and data lakes. They can ease data governance by helping CDOs with conceptual models and business terms. Their main objectives are to provide knowledge of applications, business processes, and strategic needs. They provide expertise in concept modeling.
Data Protection Officer
The DPO focuses on regulations and compliance. His primary objectives are to ensure compliance with data quality and appropriate use of data in the company. He ensures that data is relevant and safely used. All this to avoid fines from regulators.
Data users for innovation
Data Scientist
Data scientists use data to build disruptive new use cases to create a competitive advantage for a company. His primary objectives are to use reliable sources and linked data to provide innovative ideas and go quickly into production.
What is a data governance framework?
Data governance frameworks are best practice referential, and norms used by CDOs to set up and implement their data governance programs.
Several data governance frameworks exist on the market, but the Data Management Book of Knowledge (DMBok V2) is the reference. The DMBok framework is a set of best practices for Data Management created by the international DAMA association members (Data Management professionals) aiming to enhance data management collaboratively.
The DMBok defines a data management framework in 11 subdomains with best practices for each and data governance maturity level assessments. It represents a data governance certification (Certified Data Management Professional) and is linked to DMBok knowledge proficiency.
A data governance framework provides an organized and consistent approach to managing data across the organization. It helps organizations define roles and responsibilities, prioritize activities, monitor performance, and ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Additionally, a data governance framework can help organizations identify potential risks associated with their data assets and take proactive steps to reduce them. Finally, having a clear set of policies and procedures for managing data can improve efficiency by reducing duplication of effort and ensuring that everyone uses the same processes.
What are the strategic accelerators for building Business Data Governance?
Data governance tools can accelerate data governance when leveraging on synergies with other strategic initiatives. Connected with enterprise architecture features, it can provide IT portfolio and solution architecture knowledge that is needed for data governance. Moreover, knowing IT solutions changes in advance helps to handle data governance maintenance and impact analysis in the long term.
Data governance tools connected with process modeling give a business view on data life cycles: where the data is created or entered, how it is used in which context? Linking process and data governance allows the company to be more customer and performance-oriented, and to adapt to change quickly.
Data Governance must deal with data compliance and quality. When linking with the wider Governance Risk and Controls initiatives – it helps to better assess risks and impacts, data importance, and classification.
Strategic accelerators for building effective business data governance include:
- Define the Business Data Governance Strategy
- Develop a Data Governance Framework
- Set a Data Governance Team
- Define Data Quality Standards
- Establish Data Security Policies
- Implement Data Governance Tools
- Monitor and Measure Data Governance Performance
Data governance and its importance
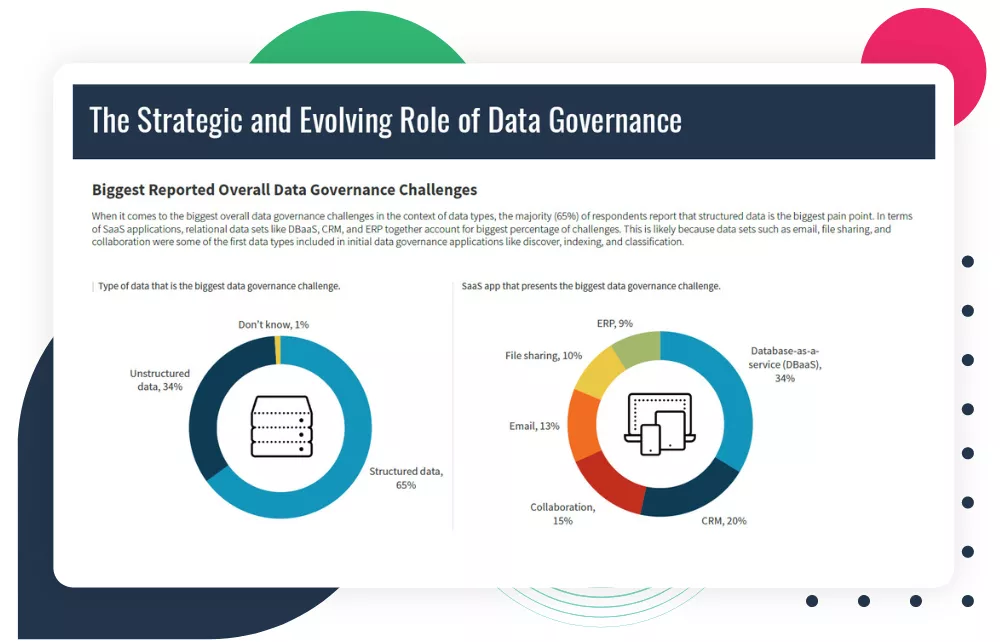
Data Governance addresses many critical company topics:
Make decisions based on reliable data aligned with the company's objectives.
A data governance program helps implement business strategies based on data. The company defines a process with different objectives and business use cases that materialize needs. It could enhance customer service levels and create new disruptive customer offers. It could be working on operational or financial performance. These use cases must be defined and prioritized with boards and different business directions.
Comply with regulations and therefore avoid heavy fines and ensure Data Security
Mastering data knowledge and usage is usually one of the most common regulatory requirements companies must face (BCBS 239, Basel III, Solvency II, GDPR, CCPA, …). These rules ensure the proper, fair, and ethical use of data for all contributors. Furthermore – Data Governance deep knowledge (where the data is stored, who is using it?) provides valuable information to enforce Data Security initiatives.
Allow Innovation based on Data.
Higher operational performance or data innovation can only be done with accurate and efficient data management. For example, Artificial Intelligence innovations can only be built with good quality data: Predictions about customer behavior need to be more stable to be used in real-life conditions.
Therefore, the data governance program's role is to organize work and use case implementation. Data must be known to be used or reused, and data quality must be ensured or enhanced. Data must be compliant with external regulations or internal policies.
By establishing uniform rules for collecting, using, storing, and sharing data, organizations can help ensure that their data is secure and accurate. Additionally, through proper data governance practices, organizations can improve efficiency by reducing costs associated with poor quality or incorrect data.
Implementing a data governance program
A data governance program is a strategic initiative that follows a continuously improving cycle. Four main steps are needed to implement a data governance program:
Step 1 – Definition of the data governance strategy
A Data Governance program is a virtuous cycle starting from companies' business needs. Business needs will help the CDO define the data governance strategy. Once the system is defined at the board level, business needs and use cases are associated with data needs by the CDO.
Step 2 - Data governance assets knowledge management
Create a new organization with internal partners and users
The Chief Data Officer or Data governance manager is here to create a new organization to support Data Management and Data usage. The Data office comprises experts like Data Stewards, Custodians, and Data Architects.
They are here first to create Data Catalogs and Business glossaries to allow data reuse. Besides, their aim is also to support business data users and implement projects. They typically work with Data Owners that are on the business side.
Focus first on the data needed to implement critical use cases
Data Stewards must define the needed data for each selected business use case. For example, have financial processes and data been compliant? Have customer offers been improved (based on customer data)? Depending on Uses Cases priorities, data governance planning can be defined to create Data Catalog and Business glossary in a step-by-step and interactive way.
Build Data asset knowledge and communicate progress with the community
Communicating data is vital for CDOs to set up a data culture (Data Literacy). Data work progress, quality, and use case successes based on data must be promoted to motivate Data reuse. With users knowing and using them, Business Glossaries and Data Catalogs can deliver their full potential as expected.
Step 3 - Data innovation with R&D
To build data innovation, business, and data scientists will start from critical use cases and perform Data Shopping to feed A.I. algorithms.
They will then use Business Glossaries to search and select Business Data that could be used together and choose related actual data from the Data Catalog (with good quality and the proper freshness). This starting point ensures that A.I. is built on stable assets to secure A.I. stability and usability in the real world.
Step 4 - Business Value creation from real Data
Once data innovation is validated in the R&D Department, it can be made available to Business users by the I.T. department. This will be leveraging Data Governance knowledge and current data in real-life systems.
In this final stage – thanks to the CDO and his Data Office's help on Data Governance for the innovation and R&D teams – Actual and actionable solutions to answer the initial Strategic goals and business uses cases identified in the first step.
Data Governance Best Practices
Best practices in Data governance involve creating and implementing policies, procedures, and processes to ensure data accuracy, integrity, and security. This includes setting up systems to monitor data quality, developing an access control system, providing backup and recovery plans, ensuring the right people have access rights, and defining roles and responsibilities.
It also involves identifying potential risks associated with data use, monitoring data usage, and maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
These best practices help organizations protect their data while leveraging its potential value. Additionally, they provide an effective way to ensure that all stakeholders involved in data collection and use are on the same page regarding how it should be used.
Learn about: The Benefits of Data Governance
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the benefits of data governance are numerous and invaluable. Organizations that implement data governance can expect a wide range of positive results, from improved decision-making to increased customer loyalty. By regularly monitoring their data processes and ensuring compliance with regulations and established policies, businesses can protect company data's security, privacy, and integrity. Data governance is the key to unlocking the potential of your organization's data resources and driving success. So why wait?
Answers to frequently asked questions
Data governance is the overall management of the availability, usability, integrity, and security of data used in an organization. It involves setting up processes and procedures to ensure that all data is appropriately managed and has a clear purpose.
Responsibilities, creating policies and standards, and monitoring compliance. They set out who is responsible for what within the organization, making a stable framework for building different processes. Policies and standards must be created to ensure that all elements of the organization adhere to the same quality when using data. Lastly, monitoring compliance ensures that everyone in the organization remains accountable for their actions when using data. Having these three roles in place, Data Governance will help create an effective environment where data can be used effectively and securely.
Data governance is essential for any organization that seeks to protect the integrity and security of its data. The best way to illustrate the implementation of data governance is through a scenario where a company has established a set of policies, procedures, and guidelines for managing its data. This includes defining who is responsible for what data, setting up access rules, and ensuring that data is collected, stored, and used following set standards. Additionally, the company must ensure that all users comply with these policies and procedures to maintain their data's security and consistency.
Data governance is an overarching strategy involving the processes, policies, and tools used to guide an organization's data-related decisions. It is focused on using data effectively and ensuring it is appropriately managed and secure. Data governance focuses on data management's strategic aspects, such as setting standards, policies, and procedures.
Its goal is to ensure that data is managed to meet organizational objectives. In contrast, data management focuses on the operational aspects of collecting data, such as storage, integration, quality control, security, backup, etc. It involves organizing and storing data, ensuring its accuracy and reliability, maintaining databases, monitoring usage patterns, etc. Data management's primary purpose is to provide timely access to accurate information for decision-making purposes. Both are essential for any organization dealing with large amounts of information, but they serve different operational functions.
To implement data governance, organizations should start by establishing a data governance team to create a strategy and roadmap. This team should include representatives from I.T., business operations, and other departments who can ensure alignment across the organization. Organizations should also create a set of policies and procedures to ensure adherence to data security and quality standards. These policies should be regularly updated and monitored to ensure they remain up to date. Finally, organizations should create an integrated system for collecting, organizing, and managing data to provide visibility into how it is used. By taking these steps, organizations can successfully implement a comprehensive data governance program that keeps their data secure and reliable.
A data governance team is a group of individuals responsible for managing, controlling, and protecting an organization's data. This team typically consists of organizational stakeholders such as I.T., operations, and business units.
They are responsible for developing and implementing policies, procedures, and systems to ensure that data remains accurate, secure, compliant, and accessible. Additionally, team members work together to create strategies for effectively utilizing data within the organization to improve business processes, reduce costs, increase efficiency, and drive Innovation.
Data governance provides a framework for leveraging data to benefit the organization in numerous ways, helping it remain competitive in today's digital landscape. Data governance is essential to organizations of all sizes, as it helps ensure data accuracy, security, and integrity.
By establishing clear policies and procedures for managing the organization's data assets, data governance helps prevent costly errors and avoid potential legal liabilities. It also allows for better decision-making by providing access to accurate information and enabling a more thorough understanding of the data. Data governance also helps ensure that an organization complies with applicable laws and regulations. Additionally, it can be used to develop strategies for improving customer experience and increasing operational efficiency.
Implement an effective data governance program
MEGA HOPEX for Data Governance
Request a demonstration of HOPEX for Data Governance, and see how you can have immediate value for your projects.